
What is IED in Substations Automation?, -IED stands for Intelligent Electronic Device, which is a type of electronic device used in substation automation systems. IEDs are designed to perform advanced functions such as protection, monitoring, and control of electrical equipment in substations.
Read Also: BCU in Substation
An IED typically contains a microprocessor, memory, and communication interfaces, and is capable of processing large amounts of data in real-time. IEDs can communicate with other devices in the substation automation system using various communication protocols, such as IEC 61850, Modbus, or DNP3.
IEDs are used to perform a variety of functions in substation automation systems, including protection functions such as overcurrent and differential protection, monitoring functions such as voltage and current measurements, and control functions such as opening and closing circuit breakers.
What is IED in Substations Automation?
IEDs are essential components of modern substation automation systems, as they provide the intelligence and processing power necessary to perform critical functions that ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems.
Read Also: IEC 101 vs IEC 104 Protocol
IED for Control

Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) are also used for control functions in substation automation systems. These devices are capable of receiving control commands and actuating devices such as circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and tap changers.
IEDs can perform different types of control functions in substations, such as:
- Sequential control: This involves executing a series of pre-defined control commands in a specific order. For example, an IED can be programmed to open a circuit breaker, wait for a certain period of time, and then close it.
- Feedback control: In this type of control, the IED receives feedback from the system and adjusts the control action accordingly. For example, an IED can monitor the voltage in a system and adjust the tap position of a transformer to maintain a desired voltage level.
- Adaptive control: This involves adjusting the control action based on changes in the system. For example, an IED can adjust the reactive power output of a generator based on changes in the load.
IEDs are used for control functions in a variety of substation automation applications, such as load shedding, voltage regulation, and fault isolation. The ability to perform advanced control functions using IEDs is an essential feature of modern substation automation systems, as it allows for more efficient and reliable operation of the electrical grid.
IED for Protection

Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) are widely used in substation automation systems for protection functions. Protection IEDs are designed to detect abnormal conditions in the power system and isolate faulty equipment to prevent damage to the system.
Read Also: How to Update Siemens SIPROTEC 5 Firmware
Protection IEDs can perform different types of protection functions, such as:
- Overcurrent protection: This involves detecting overcurrent conditions and opening circuit breakers to isolate faulty equipment.
- Differential protection: In this type of protection, the IED compares the current entering and leaving a protected zone and activates a trip signal if there is a difference beyond a specified limit.
- Distance protection: This involves measuring the time taken for a fault current to travel from the substation to a fault location and using this information to determine the distance to the fault.
- Transformer protection: This involves monitoring various parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature to detect abnormal conditions in transformers and activate protection measures.
IEDs used for protection functions are critical components of substation automation systems, as they help to prevent equipment damage and ensure the safe and reliable operation of the electrical grid. Protection IEDs can communicate with other devices in the substation automation system to share protection data, enabling rapid response to abnormal conditions and improving the overall system reliability.
IED for Monitoring
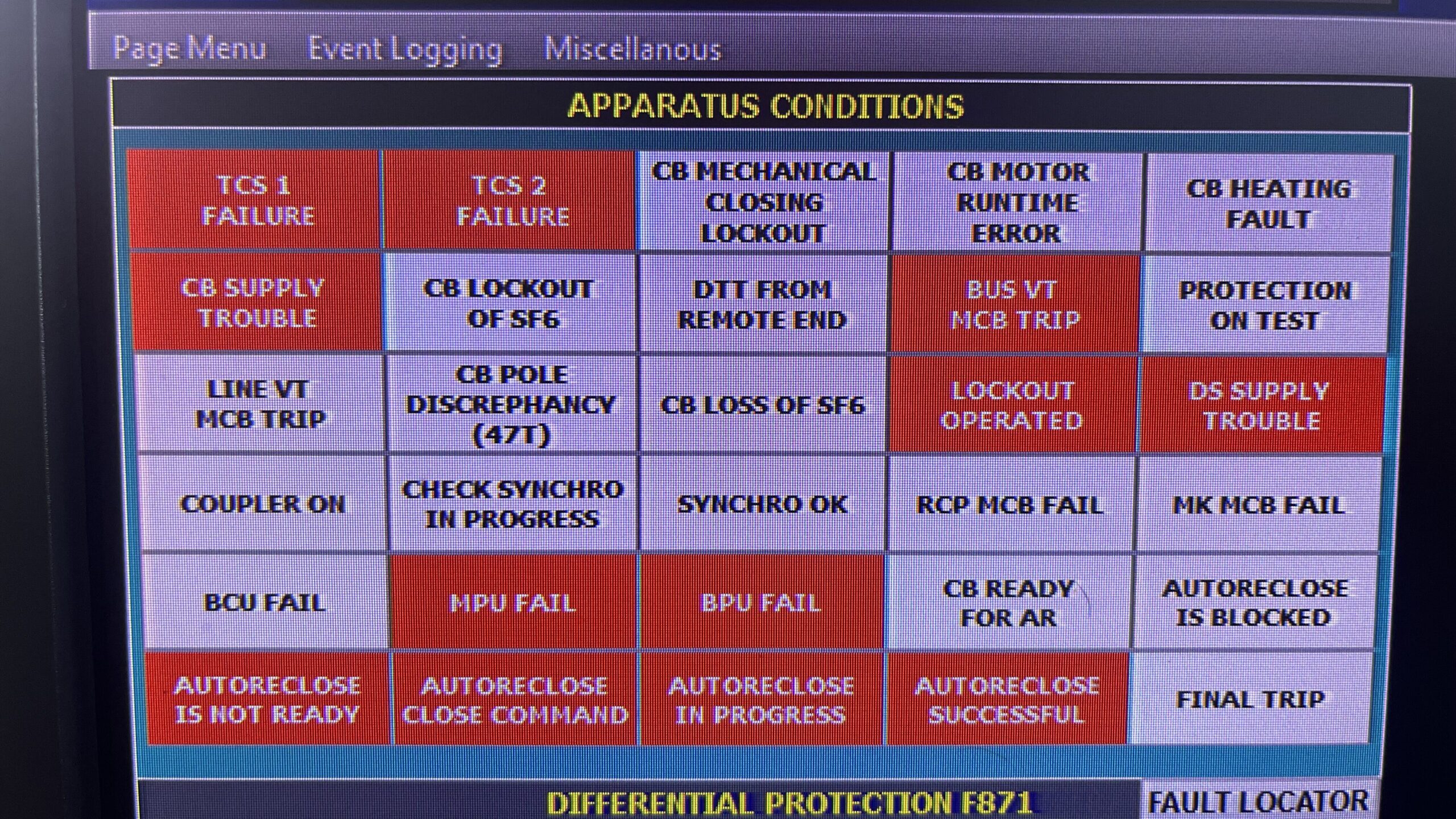
Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) are also used for monitoring functions in substation automation systems. Monitoring IEDs are designed to measure various parameters and provide real-time data on the condition of the equipment in the substation.
Monitoring IEDs can perform different types of monitoring functions, such as:
- Voltage and current measurement: This involves measuring the voltage and current levels in the power system to monitor load and detect abnormal conditions.
- Temperature measurement: Monitoring IEDs can measure the temperature of various equipment, such as transformers and switchgear, to detect abnormal heating and prevent equipment damage.
- Power quality measurement: This involves measuring parameters such as harmonic distortion, power factor, and voltage sag to ensure that the power system meets certain quality standards.
- Fault recording: This involves recording detailed information about system faults, such as the time, duration, and location of the fault, as well as the associated waveforms.
Monitoring IEDs provides valuable information for substation operators and engineers, allowing them to monitor the health of the equipment, detect potential problems before they escalate into major issues, and improve the overall system performance. The real-time data provided by monitoring IEDs can be used to optimize the operation of the electrical grid, reduce downtime, and enhance system reliability.
IED Communication Protocols

Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) in substation automation systems use various communication protocols to exchange data with other devices in the system. Some of the commonly used communication protocols for IEDs are:
IEC 61850: This is a standard protocol for substation automation systems that defines a unified approach to data modeling, communication, and system configuration. IEC 61850 allows IEDs to communicate using Ethernet-based networks and provides a standardized data model for system data.
Modbus: This is a protocol widely used in industrial automation systems, including substation automation. Modbus allows IEDs to communicate over serial communication links and Ethernet-based networks and provides a simple, standardized way of exchanging data between devices.
DNP3: This is a protocol widely used in the utility industry for communication between IEDs and remote control centers. DNP3 provides a standardized way of exchanging data over serial communication links and TCP/IP networks and supports features such as time synchronization and event reporting.
Profibus: This is a protocol widely used in industrial automation systems that enables IEDs to communicate over a serial bus network. Profibus provides high-speed communication and supports a variety of data transmission rates.
The choice of the communication protocol for IEDs depends on various factors such as the specific application, the communication network infrastructure, and the compatibility with other devices in the system. The use of standardized communication protocols allows IEDs from different manufacturers to communicate with each other and provides flexibility in system configuration and integration.

You must be logged in to post a comment.